Project
Background
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is an unpredictable and potentially deadly condition and should be promptly treated with catheter ablation and medication, before irreversible and potentially fatal organ damage follows. Unfortunately, this combination of treatments does not prevent VT reoccurrence in 30-50% of VT patients and while they can undergo multiple invasive ablations, technical difficulties or refusal of the patient can lead to a lack of effective treatment options.
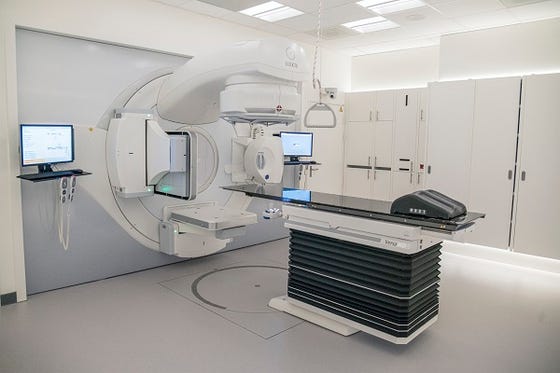
A promising novel, non-invasive treatment option for VT is stereotactic arrhythmia radioablation (STAR). Besides being non-invasive, STAR can also be used to reach locations that are inaccessible for catheter ablation, which may potentially improve effectiveness of overall VT treatment.
Small scale first in men/early phase trials have been performed for STAR, providing proof-of-concept for clinical safety and efficacy. However, patients with recurrent VT are not a homogenous group and each center deals with different inclusion criteria, imaging and/or target definition. Many questions remain and the available studies lack the power to clinically validate the approach and prepare for late stage phase III trials.
Approach
The STOPSTORM consortium sets out to consolidate all current and future European efforts to clinically validate STAR treatment by merging all data in a validation cohort study, standardising pre-treatment and follow-up, in order to collect the data sets and statistical power needed to unanimously establish clinical safety, efficacy and benefit for STAR.
The STOPSTORM consortium also sets out to refine protocols and guidelines, determine volumes of interest, define and model the optimal target region and target dose, also in relation to surrounding healthy tissues (i.e. organs at risk) and determine which patient population and underlying cardiopathies respond best to STAR.
Mission
By doing so the STOPSTORM consortium paves the way to consensus and future late stage clinical trials for STAR.
